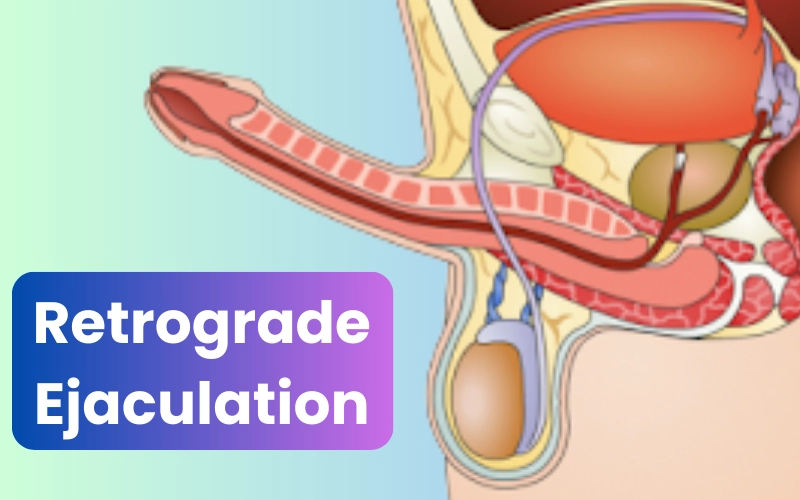
Retrograde ejaculation is a rare yet important condition where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis during orgasm. While it doesn’t cause pain or prevent orgasm, it can lead to fertility issues and signal underlying medical concerns.
What Is Retrograde Ejaculation?
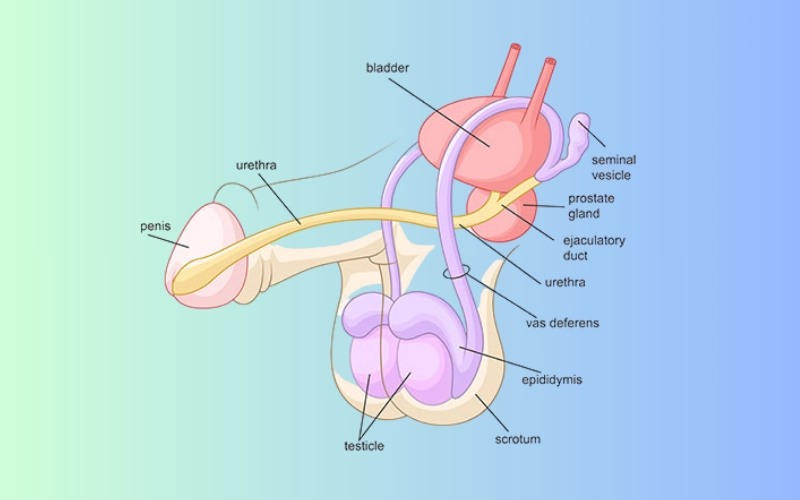
Retrograde ejaculation is a condition in which semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis during orgasm. This results in a “dry orgasm,” where little or no semen is ejaculated externally, even though the pleasurable sensation of orgasm still occurs.
This condition is not harmful and does not usually affect sexual pleasure or the ability to have an erection. However, it can cause fertility problems for men who are trying to conceive, as the sperm is not expelled from the body.
Retrograde ejaculation occurs when the muscles of the bladder neck (internal sphincter) fail to close properly during ejaculation. Instead of propelling semen outward through the urethra, the semen flows backward into the bladder.
What Causes Retrograde Ejaculation?
Retrograde ejaculation can result from various factors that interfere with the normal function of the bladder neck muscles. These causes generally fall into three main categories: medical conditions, medications, and surgical procedures.
1. Medical Conditions
Certain health conditions can affect the nerves or muscles that control ejaculation, including:
- Diabetes: A leading cause due to nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy) affecting the bladder sphincter.
- Multiple sclerosis (MS): Can disrupt nerve signals involved in ejaculation.
- Spinal cord injuries: Damage to nerves may alter the function of the bladder and reproductive system.
- Parkinson’s disease: A neurodegenerative disorder that can interfere with autonomic nervous system function.
2. Medications
Several drugs can interfere with the closure of the bladder neck during ejaculation:
- Alpha-blockers (used to treat high blood pressure or prostate enlargement)
- Certain antidepressants and antipsychotics
- Medications for enlarged prostate such as tamsulosin
These medications relax smooth muscles, including those at the bladder neck, allowing semen to flow backward.
3. Surgical Procedures
Retrograde ejaculation can also occur as a side effect of surgeries that involve the bladder, prostate, or spinal cord, including:
- Prostate surgery (e.g., TURP – transurethral resection of the prostate)
- Bladder neck surgery
- Spinal surgeries affecting autonomic nerves
What Are the Symptoms of Retrograde Ejaculation?
The primary symptom of retrograde ejaculation is the absence or noticeable reduction of semen expelled during orgasm (a condition known as dry orgasm), despite normal sexual stimulation and orgasmic sensation.
Common Signs and Symptoms:
- Little to no semen during ejaculation
- Cloudy urine after orgasm (due to semen mixing with urine in the bladder)
- Fertility issues (difficulty achieving pregnancy despite regular intercourse)
- Normal orgasm and erection are usually preserved
📌 Important Note: Retrograde ejaculation is typically not harmful to a man’s overall health or sexual pleasure, but it can significantly affect fertility.
When to Seek Medical Help:
- If you experience persistent dry orgasms
- If you’re attempting to conceive and facing unexplained infertility
- If the change in ejaculation occurs after surgery or starting a new medication
Risk Factors
Although retrograde ejaculation is relatively uncommon, certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing this condition. These risk factors typically relate to underlying medical conditions, surgical history, or the use of specific medications.
Common Risk Factors Include:
- Diabetes Mellitus
Poorly controlled diabetes, particularly type 1 and type 2, can damage the nerves and muscles that regulate bladder and sphincter function, increasing the risk of retrograde ejaculation. - Prostate or Bladder Surgery
Surgical procedures such as prostatectomy (removal of the prostate), bladder neck surgery, or transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) can disrupt the normal pathway of ejaculation. - Spinal Cord Injury
Injuries affecting the spinal cord can impair nerve signals needed for proper ejaculatory function. - Use of Certain Medications
Drugs that affect the nervous system or muscle tone in the bladder neck may contribute to retrograde ejaculation. These include:Alpha-blockers (e.g., tamsulosin) used for enlarged prostate
Antidepressants
Antipsychotics
Antihypertensives
- Neurological Conditions
Disorders such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and neuropathy can interfere with the coordination required for normal ejaculation. - Aging
Older men may be more prone to retrograde ejaculation due to age-related nerve and muscle changes.
⚠️ Note: While some of these risk factors are unavoidable, others—such as managing diabetes or reviewing medications—can be addressed with the help of a healthcare provider.
How Is Retrograde Ejaculation Diagnosed?
Diagnosing retrograde ejaculation involves understanding the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and confirming the presence of semen in the bladder after orgasm. Since this condition is often overlooked or misdiagnosed, a thorough and specific evaluation is essential.
1. Medical and Sexual History
A healthcare provider will begin by asking detailed questions, such as:
- Are you experiencing dry orgasms (no semen release)?
- When did the symptoms start?
- Have you undergone any recent surgeries (especially prostate or bladder)?
- Do you have diabetes or take medications that might affect ejaculation?
- Is fertility a concern?
2. Physical Examination
A general physical exam helps check for any abnormalities in the genital or pelvic region and assess nerve function that may influence ejaculation.
3. Post-Ejaculatory Urinalysis
This is the most definitive test for retrograde ejaculation. It involves:
- Asking the patient to provide a urine sample shortly after orgasm.
- The urine is then analyzed under a microscope to detect sperm cells.
✅ If sperm is found in the urine, it confirms retrograde ejaculation.
❌ If no sperm is found, other causes of dry orgasm may be considered, such as:
- Anejaculation (complete absence of ejaculation)
- Obstruction in the ejaculatory ducts
4. Additional Tests (if needed)
If the diagnosis remains unclear, further evaluations may include:
- Hormonal blood tests – to rule out endocrine causes
- Urodynamic studies – to assess bladder function
- Imaging (e.g., ultrasound) – if obstruction is suspected
🔍 Accurate diagnosis is especially important for men experiencing fertility issues or those with a recent history of pelvic surgery.
Treatment Options for Retrograde Ejaculation
Treatment for retrograde ejaculation depends on the underlying cause, severity, and whether fertility is a concern. In many cases, it can be managed effectively through medication, lifestyle adjustments, or assisted reproductive techniques.
1. Treating Underlying Conditions
If the condition is caused by diabetes, nerve damage, or surgery, addressing the root cause is the first step:
- Diabetes control: Managing blood glucose levels may improve nerve function over time.
- Medication adjustment: If ED or antidepressant medications are the cause, doctors may adjust or substitute them with alternatives.
2. Medications
Certain medications can help tighten the bladder neck muscle, encouraging semen to move forward during ejaculation instead of backward into the bladder:
| Medication | How It Works | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Alpha-agonists | Increase bladder neck tone | Pseudoephedrine, Imipramine |
| Anticholinergics | Relax bladder muscle to promote forward ejaculation | Brompheniramine |
⚠️ These medications are not always effective for everyone and may have side effects like high blood pressure, insomnia, or dry mouth.
3. Assisted Reproductive Techniques (for Fertility)
If the main concern is infertility due to retrograde ejaculation, several fertility techniques can help:
- Sperm Retrieval from Urine: After orgasm, sperm is collected from urine and processed for insemination.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Retrieved sperm is inserted directly into the uterus.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): A more advanced option, especially if sperm count or quality is low.
💡 Doctors may advise alkalinizing the urine (e.g., with sodium bicarbonate) before ejaculation to help preserve sperm quality in the bladder.
4. Psychological Support
Although retrograde ejaculation is not painful or harmful, it may cause distress or self-esteem issues. In such cases:
- Counseling: Helps address concerns about masculinity or fertility.
- Couples therapy: Encourages open communication with partners about intimacy and treatment options.
Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Changes for Retrograde Ejaculation
While retrograde ejaculation is often caused by nerve damage or medical treatments that require professional care, there are certain natural approaches and lifestyle habits that may help improve overall sexual function and, in some cases, support recovery of ejaculation control.

1. Improve Nerve Health
Since nerve function plays a critical role in controlling ejaculation and bladder neck closure, protecting your nervous system is essential.
- Control blood sugar: Especially important for men with diabetes to prevent or limit nerve damage.
- Vitamin B12 and Alpha-lipoic acid: May help support nerve regeneration (consult your doctor before taking supplements).
- Avoid neurotoxic substances: Limit alcohol and stay away from recreational drugs that can impair nerve signals.
2. Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegel Exercises)
Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles may help in regaining better control of ejaculation.
- Practice tightening the muscles you use to stop urination midstream.
- Perform 10–15 repetitions, 2–3 times daily.
💡 Kegels can also improve erectile function and bladder control.
3. Reduce Stress and Anxiety
Chronic stress may contribute to poor sexual performance and hormonal imbalances.
- Try yoga, deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness meditation.
- Reduce work overload and prioritize restful sleep.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity and metabolic syndrome can contribute to both nerve and hormonal dysfunctions. Losing weight may improve:
- Insulin sensitivity
- Testosterone levels
- Circulatory and nerve function
5. Limit Substances That Affect the Nervous System
- Caffeine and nicotine may overstimulate the nervous system, while alcohol can suppress it.
- Moderation is key if complete avoidance isn’t possible.
6. Consider Natural Supplements (With Caution)
Some herbal supplements may help improve nerve health, blood flow, or hormonal balance. Always consult a healthcare provider before use.
| Supplement | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
| Panax Ginseng | May improve sexual performance |
| Maca Root | Known for enhancing libido |
| Zinc & Vitamin D | Support hormone balance and function |
| Ashwagandha | May reduce stress and support hormones |
| L-Carnitine | Supports nerve regeneration in some studies |
⚠️ These are not specific cures for retrograde ejaculation, but they may support overall reproductive health when used appropriately.
Can Retrograde Ejaculation Be Prevented?
In many cases, retrograde ejaculation cannot be entirely prevented—especially when it results from unavoidable medical conditions or surgeries. However, there are steps that men can take to reduce the risk or minimize the severity of this condition.
1. Manage Underlying Health Conditions
Several chronic health issues, especially those affecting the nervous system, can contribute to retrograde ejaculation. Managing these conditions early and effectively is essential:
- Diabetes mellitus: Keep blood sugar under control to avoid long-term nerve damage.
- Multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease: Follow your treatment plan closely to reduce progression and nerve involvement.
2. Use Medications with Caution
Some medications, such as alpha-blockers or antidepressants, can interfere with the bladder neck’s ability to close properly. You can lower your risk by:
- Consulting your doctor before starting any new medication
- Reporting sexual side effects early to explore alternatives
⚠️ Never stop prescribed medications without medical supervision, but be proactive in discussing sexual health concerns with your healthcare provider.
3. Avoid Unnecessary Pelvic or Prostate Surgery
While certain surgeries are medically necessary, it’s important to:
- Understand the potential risks of retrograde ejaculation before undergoing procedures like TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate) or bladder surgeries.
- Discuss nerve-sparing techniques with your surgeon, if available.
4. Maintain Healthy Habits
Keeping your nervous and vascular systems in good shape supports better sexual function overall:
- Exercise regularly to enhance circulation and nerve health
- Eat a balanced diet to support hormonal and metabolic function
- Limit alcohol and avoid smoking, both of which can worsen nerve and bladder function
Retrograde Ejaculation vs. Other Ejaculation Disorders
Retrograde ejaculation (RE) is one of several types of ejaculation disorders that affect male sexual health. Understanding how it differs from other common conditions can help ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
| Feature | Retrograde Ejaculation | Premature Ejaculation (PE) | Delayed Ejaculation (DE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Semen enters the bladder instead of exiting the penis | Ejaculation occurs too quickly (usually within 1–2 minutes) | Ejaculation is significantly delayed or absent despite adequate stimulation |
| Ejaculate Presence | Absent or very little semen during orgasm | Present but occurs too early | May occur after long delay or not at all |
| Causes | Nerve damage, surgery, medications | Psychological, neurological, or sensitivity-related | Psychological issues, medications (e.g. SSRIs), or neurological damage |
| Orgasm Sensation | Normal orgasm sensation, but no semen expelled | Orgasm occurs, but quickly | Orgasm may be difficult to reach or delayed |
| Common Triggers | Prostate surgery, diabetes, alpha-blockers | Anxiety, stress, hypersensitivity | Antidepressants, chronic stress, prostate surgery |
| Fertility Impact | May cause infertility due to lack of external ejaculation | Usually does not affect sperm quality | May affect conception if ejaculation does not occur |
Key Takeaway:
- Retrograde Ejaculation is unique in that orgasm still occurs, but ejaculate is misdirected into the bladder.
- Unlike PE or DE, which affect timing or ability to ejaculate, RE involves a mechanical misrouting of semen due to muscle or nerve dysfunction.
🔍 Accurate diagnosis is essential, as treatment approaches differ for each condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is retrograde ejaculation dangerous?
No, retrograde ejaculation is not physically harmful. However, it can impact fertility and may be a symptom of an underlying condition, such as diabetes or nerve damage. If you’re trying to conceive or experiencing other symptoms, it’s important to consult a doctor.
2. Can retrograde ejaculation be reversed?
In some cases, yes. If caused by medications, stopping or switching drugs may help. If due to nerve damage, treatment can be more complex. Certain medications or assisted reproductive techniques can also help manage fertility issues related to RE.
3. Does retrograde ejaculation affect orgasm?
No. Men with retrograde ejaculation usually experience normal orgasm sensations. The difference is that little to no semen is expelled through the penis during climax.
4. Is retrograde ejaculation common after prostate surgery?
Yes. Procedures like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) often disrupt the internal sphincter that controls ejaculation, leading to retrograde ejaculation in many men post-surgery.
5. Can I still father a child if I have retrograde ejaculation?
Natural conception may be difficult due to semen entering the bladder. However, fertility treatments such as sperm retrieval from the urine and intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) are possible options.
6. How is retrograde ejaculation diagnosed?
A post-ejaculation urine test is typically used. If sperm is found in the urine, it confirms the diagnosis.
7. Can lifestyle changes help with retrograde ejaculation?
While lifestyle changes may not directly reverse RE, managing underlying conditions like diabetes or avoiding certain medications can reduce the risk. Healthy habits also support overall sexual and reproductive health.
Summary & Final Thoughts
Retrograde ejaculation may not be a life-threatening condition, but its impact on fertility and sexual confidence can be significant. While it often goes unnoticed due to the presence of orgasm, the absence or reduction of semen can be alarming — and for couples trying to conceive, it can be a major obstacle.
Fortunately, retrograde ejaculation is both diagnosable and, in many cases, manageable. From identifying and addressing underlying causes like diabetes or medication side effects, to exploring treatments such as targeted medications or assisted reproductive techniques, there are multiple paths forward.
If you suspect you’re experiencing retrograde ejaculation, don’t hesitate to seek help. An open conversation with a healthcare provider can offer clarity, reassurance, and a roadmap toward effective treatment.
Remember: Your sexual health is an essential part of your overall well-being — and taking action today could make all the difference tomorrow.